In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, maintaining a robust safety culture is not just a regulatory requirement—it’s a cornerstone of operational excellence. At The Safety Master, we understand that Process Safety Management (PSM) is crucial in preventing incidents and ensuring a safer working environment. This article explores essential strategies to master PSM and enhance workplace safety.
What is Process Safety Management?
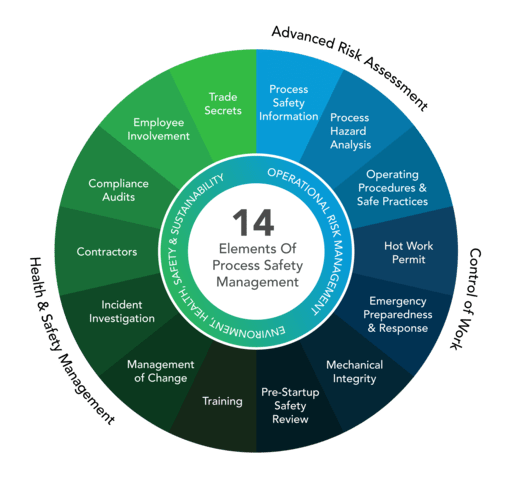
Process Safety Management (PSM) is a systematic approach to managing the integrity of hazardous processes and chemicals. It involves the identification, assessment, and control of risks associated with process operations to prevent accidents and incidents. PSM encompasses a range of practices, from hazard analysis and risk assessment to safety training and emergency response planning. Its goal is to safeguard both people and assets while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
The Core Elements of Process Safety Management
To master PSM effectively, it is essential to understand its core elements, which typically include:
- Process Safety Information (PSI): Comprehensive documentation about the chemicals, equipment, and processes used in operations. This information forms the foundation for hazard analysis and risk assessment.
- Process Hazard Analysis (PHA): A systematic examination of the processes to identify and evaluate potential hazards. Techniques like HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) and FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) are commonly used.
- Operating Procedures: Detailed instructions for operating processes safely. These procedures should be clear, accessible, and regularly updated.
- Training: Ensuring that employees are adequately trained in both the technical aspects of their roles and the safety procedures relevant to their work.
- Mechanical Integrity: Regular inspection, testing, and maintenance of equipment to ensure it functions correctly and safely.
- Management of Change (MOC): Procedures for managing changes to processes, equipment, or operations to assess and mitigate potential risks associated with these changes.
- Incident Investigation: Procedures for investigating incidents and near misses to understand their causes and prevent recurrence.
- Emergency Planning and Response: Developing and implementing plans for responding to emergencies effectively.
- Audits and Reviews: Regular audits and reviews of the PSM system to ensure its effectiveness and compliance with regulations.
- Employee Participation: Involving employees at all levels in the PSM process to leverage their insights and experiences.
Essential Strategies for Mastering PSM
1. Develop a Strong Safety Culture
A strong safety culture is the backbone of effective PSM. It starts with leadership commitment and cascades down to every employee. At The Safety Master, we emphasize the importance of leadership in setting the tone for safety. Leaders should actively promote safety, model safe behaviors, and encourage open communication about safety concerns. Regular safety meetings, recognition programs, and a transparent reporting system are also vital in fostering a safety-conscious environment.
2. Implement Comprehensive Training Programs
Training is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Employees must be equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to perform their jobs safely. The Safety Master recommends creating a robust training program that includes initial training for new hires, refresher courses, and specialized training for different roles. Use a mix of theoretical and practical training methods, including simulations and hands-on exercises, to enhance learning.
3. Conduct Regular Hazard Analysis
Regular hazard analysis is crucial for identifying potential risks and implementing appropriate controls. At The Safety Master, we advise using a systematic approach to hazard analysis, such as HAZOP or FMEA, tailored to the specific needs of your organization. Ensure that hazard analyses are updated regularly and whenever there are significant changes to processes or equipment.
4. Maintain Rigorous Mechanical Integrity
Mechanical integrity is vital for preventing equipment failures that can lead to accidents. Implement a preventive maintenance program that includes regular inspections, testing, and repairs. The Safety Master recommends using predictive maintenance technologies and maintaining detailed records of all maintenance activities. This approach helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate.
5. Develop a Robust Management of Change (MOC) Process
Changes to processes, equipment, or operations can introduce new hazards. A well-defined MOC process ensures that all changes are assessed for their impact on safety before implementation. At The Safety Master, we emphasize the importance of involving relevant stakeholders in the MOC process and documenting all changes comprehensively.
6. Invest in Effective Emergency Planning and Response
Preparedness is key to managing emergencies effectively. Develop and regularly test emergency response plans to ensure they are up-to-date and practical. Conduct drills and simulations to familiarize employees with emergency procedures and identify areas for improvement. The Safety Master advises integrating lessons learned from drills and real incidents into the emergency response plan.
7. Regularly Audit and Review PSM Systems
Regular audits and reviews are essential for maintaining the effectiveness of PSM systems. Conduct internal and external audits to assess compliance with regulations and identify areas for improvement. At The Safety Master, we recommend using audit findings to drive continuous improvement in PSM practices.
8. Engage Employees in Safety Initiatives
Employee participation is a crucial element of PSM. Encourage employees to actively participate in safety programs, report hazards, and contribute to safety discussions. Creating a safety committee or task force that includes representatives from different departments can help in addressing safety concerns more effectively.
Conclusion
Mastering Process Safety Management requires a comprehensive approach that integrates strong leadership, rigorous procedures, and continuous improvement. At The Safety Master, we are committed to helping organizations implement and refine their PSM systems to create safer workplaces. By adopting these essential strategies and fostering a culture of safety, you can enhance your organization’s safety performance and protect your most valuable assets—your people and your operations.
Implementing effective PSM practices not only ensures regulatory compliance but also contributes to the overall success and sustainability of your organization. Remember, safety is not a destination but a continuous journey, and with the right strategies, you can navigate this journey successfully.